Patch Management
What is Patch Management?
A patch is a piece of software code applied after the software program is installed to rectify an issue within it. Generally, the software applications roll out several patches after their initial release and keep on releasing the versions to fix any vulnerabilities or bugs in an application. Patch management is the process of managing a network of computers by regularly distributing and applying the updates to software. These patches are often necessary to correct errors.
Benefits
For organizations owning multiple servers and computers, updating patches manually can be both time-consuming and challenging. It can also increase business risks if any critical vulnerability is left unforeseen. The following are the few reasons why Patch Management should be considered:
- Security: It fixes vulnerabilities on software and applications that are susceptible to cyber-attacks, helping the organization reduce its security risk.
- System Reliability: It ensures that software and applications are updated and run smoothly.
- Feature and Functional Improvements: It can go beyond application fixes by providing updates in its feature or functionality.
- Compliance: With the continuous rise in cyber-attacks, organizations require to maintain a certain level of compliance. Patch management is a necessary piece of adhering to compliance standards.
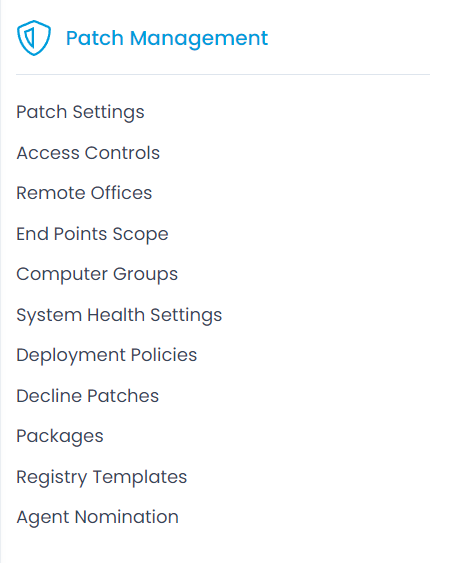
Patch Management group has the options that are specific to customize the Patch module. It has the following features:
- Patch Settings: Customize the settings of the patch configuration.
- Remote Offices: Manage the computers for different locations.
- End Points Scope: Manage the end points and their Scope for the Patch Module.
- Computer Groups: Manage the computer groups for processing that complies with your configuration.
- System Health Settings: Customize the settings of the System's Health.
- Deployment Policies: Define the various policies for the Deployment.
- Decline Patches: Customize the singleton or the group of Patches for declining while deploying.
- Packages: Arrange and create different packages supporting the programs for the servers.
- Registry Templates: Select or create different templates for deployment.
- Agent Nomination: Select the agents for nomination.