DC-DR Server Setup
A DC-DR setup, which stands for a Data Center (DC) and Disaster Recovery (DR) setup, entails establishing a system wherein organizations duplicate their important IT infrastructure, applications, and data in a secondary data center or location. This duplication aims to guarantee uninterrupted business operations in case of a disaster or unforeseen disruption in the primary data center.
The main objective of a DC-DR setup is to reduce downtime and uphold the functionality of crucial services, even during a major incident that impacts the primary data center.
Architecture
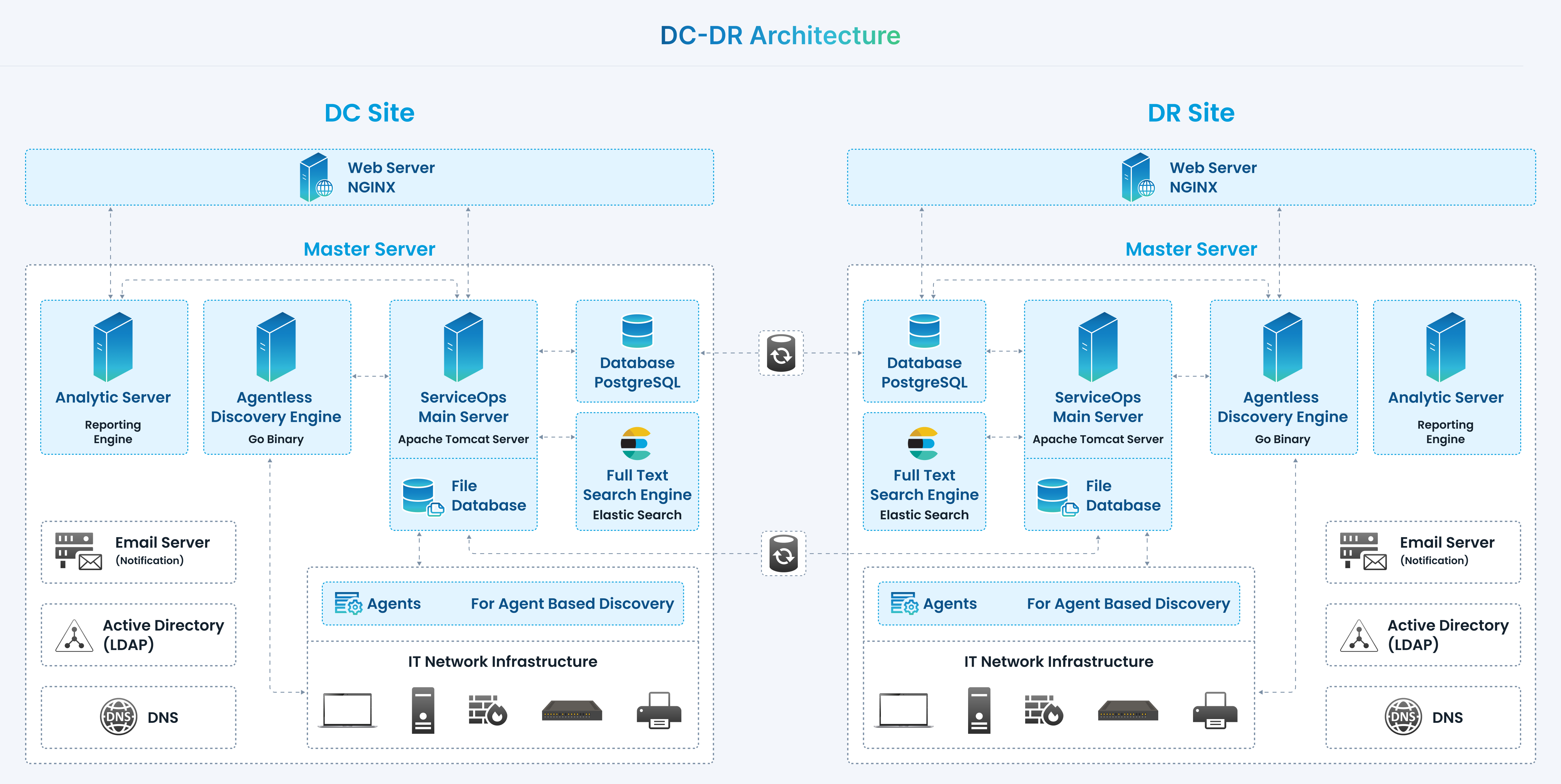
ServiceOps recommends the Disaster Recovery site set up to avoid complete data loss in case any disaster occurs on the DC site.
As a part of the DC-DR site setup, perform the following activity daily to replicate/back up the latest data from the DC-DR site.
- Continuous Replication of Database
- Continuous Replication of File Attachments Storage
When the DC site is down, the following manual steps must be performed on the DR site for business continuity:
- Database Switch over (Converting Slave to Master)
- Start Application Services and redirect DNS traffic to DR site
Application also provides support of automated regular back of database at a distributed location using FTP, as an additional security measure.
Replication of Database and File Attachment Storage Data
Database Replication between DC and DR
To configure continuous database replication to the DR site, follow the below steps.
Prerequisites:
- Continuous connectivity to transfer data from DC to DR sites.
- ServiceOps application versions of DC and DR must be the same.
- SSH port must be accessible.
- Database port must be accessible.
Implementation Steps to be performed on the DC site Database Server:
Login using the root user.
Download the CommonDCDR.zip file, extract it and move the Motadata_DC_Setup file to the /home directory.
Change permission of the setup file and run Motadata_DC_Setup using the following command
chmod 777 Motadata_DC_Setup
./Motadata_DC_Setup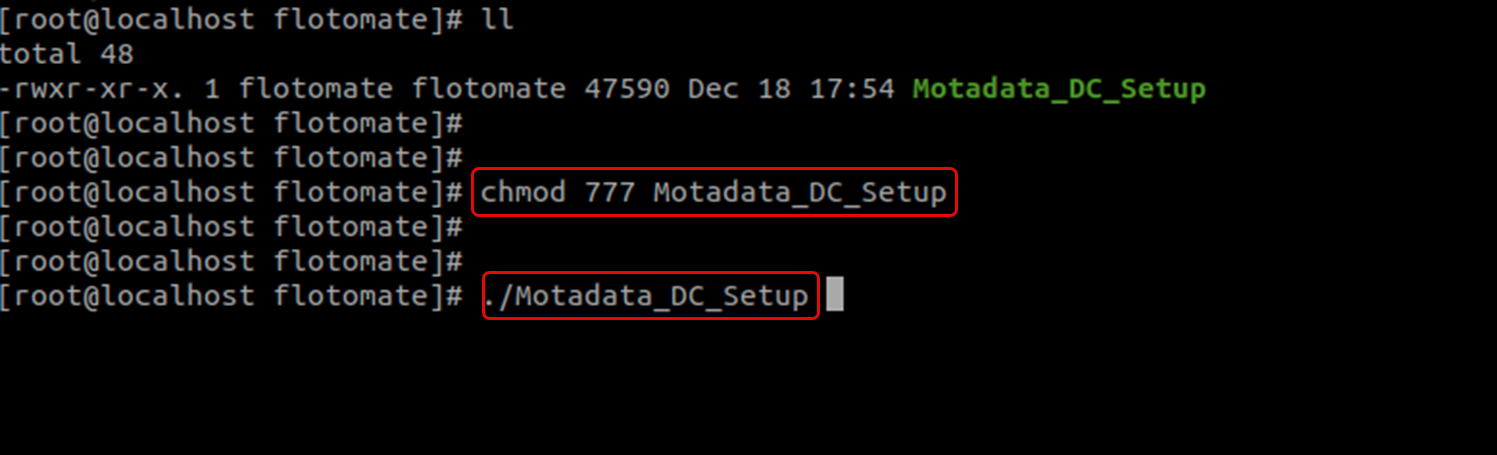
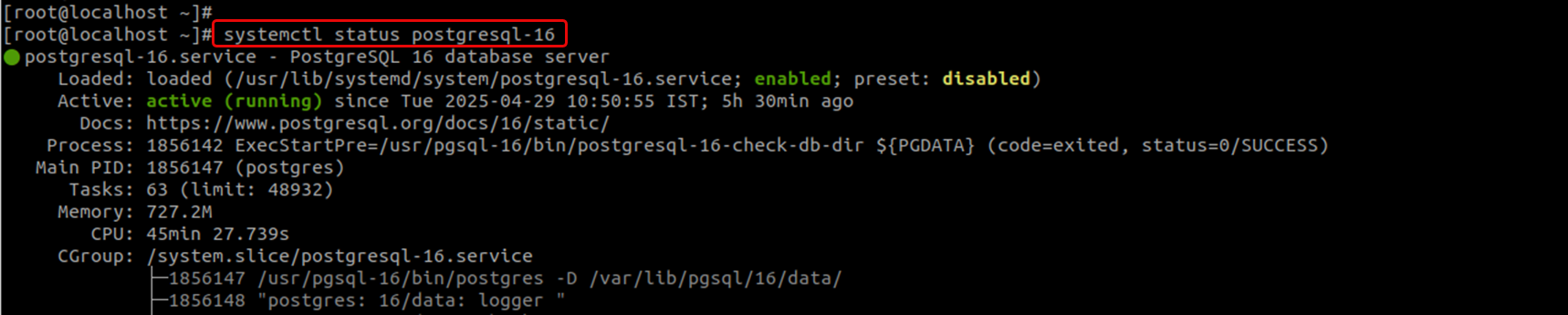
Check Postgres Service Status using the following command.
systemctl status postgresql-16
Implementation Steps to be performed on the DR site Database Server:
- Login using the root user.
- Download the CommonDCDR.zip file, extract it, and move the Motadata_DR_Setup file to the /home directory.
- Change permission of the setup file and run Motadata_DR_Setup using thr following command.
chmod 777 Motadata_DR_Setup
./Motadata_DR_Setup {Master Database IP Address}

Check Postgres Service Status using the following command.
systemctl status postgresql-16
Attachment Files Replication on DR site
To configure continuous Attachment Files data replication to the DR site, follow the below steps.
Prerequisites:
Continuous connectivity to transfer data from DC to DR sites.
SSH port should be accessible.
ServiceOps application versions of DC and DR must be the same.
Ownership should be fmtuser:fmtusergroup
chown -R fmtuser:fmtusergroup /opt/flotomate/main-server/filedb
Implementation Steps to be performed on the DC site Application Server:
Login root user.
Go to the file path: /opt/HA/slave.sh and rename this file to slave.sh.bkp
mv /opt/HA/slave.sh /opt/HA/slave.sh.bkpDownload the Modatada_HA_Setup file and move to /home/{common sudo user}
Login common sudo user.
Change the Motadata_HA_Setup file permission using the below command.
chmod 777 Motadata_HA_SetupRun Motadata_HA_Setup using the below command.
./Motadata_HA_Setup

Edit /opt/HA/file-sync.sh file and add the below details:
current_slave: IP address of the DR server.
user=SSH username.
password= SSH password.
port=SSH port number.
Start the file sync service using the below command:
systemctl start file-sync.serviceCheck the status of the service using the below command:
systemctl status file-sync.service
Manual switching to the DR Site (when DC is down)
When the DC site is down, the following manual steps must be performed on the DR site for business continuity.
Switch Slave to Master DB:
Login root user.
Go to the /opt directory and execute the master_db.sh file.
sh master_db.shCheck the Postgresql service status using the below command.
systemctl status postgresql-16
Start Application:
Once the database is restored, start the Main Server and Analytics Server services using the below commands:
systemctl start ft-main-server
systemctl start ft-analytics-server
systemctl start ft-plugins-serverOnce the application is up and running, redirect DNS to DR site.
Login to the application for sanity check.
Convert Old DC to New DR for Switch Back (when Old DC is Up)
Once the Old DC site is recovered and you want to convert the Old DC site to new DR site, perform the following steps.
Database Synchronization between New DC-DR
Implement the below steps on the Old DC (New DR) site Database Server.
Perform the below steps immediately once the old DC is up.
Login with the root user.
Download the Motadata_DR_Setup and move to the /home directory.
Change the permission of the setup file and run Motadata_DR_Setup using the following command.
chmod 777 Motadata_DR_Setup
./Motadata_DR_Setup {Master Database IP Address}Check the Postgres service status using the following command.
systemctl status postgresql-16

Start Application (Optional):
- Once the database is restored, stop the Main Server and Analytics Server services using the below commands:
systemctl stop ft-main-server
systemctl stop ft-analytics-server
systemctl stop ft-plugins-server - Once the application is up and running, redirect DNS to the New DR site.
- Log into it to application for sanity check.
Database Backup & Restoration
ServiceOps application supports automated scheduled database backup to different locations via FTP. Daily backup scheduling is recommended to minimize data loss in any disaster.
Database Backup Configuration
The following configurations must be done in ServiceOps to schedule regular backups of the database:
- Login to the ServiceOps application.
- Go to Admin > Orgainzation > Application Maintenance menu and click on the Database Backup tab.
- Configure Database Backup Settings to export the database backup to a specific FTP location (FTP applies only to Linux machines).

- Enter the Host name, Username, Password, and Folder Path where the backup is to be stored. Once configured, test the connectivity to the FTP server using the Test Connection button.
- Enter the number of backups that you want to store. Once the limit exceeds, the oldest backup will be deleted first. The default value is 10. The minimum limit is 5, and a maximum of 99 backups can be retained.
- Once done, click Update.
- Schedule Database Backup: Set the database backup schedule as daily. Also, specify the date and time when the schedule should start in the Start At field. Additionally, specify the Time at which the schedule should run.

- Test the Backup Process by clicking on Backup Now. Upon successful backup process completion, a history record will be created and displayed on the database backup listing page.

Restore Database Manual (Optional If Required)
To restore the database, perform the below steps on DR,
Download and move the latest database backup (pgdump) file to the /tmp folder using the command:
mv DB_DATE_BACKUP.zip /tmp/
cd /tmp
unzip DB_DATE_BACKUP.zipFor example:
mv DB_10-6-2021_11-00-00_pm.zip /tmp
cd /tmp
unzip DB_10-6-2021_11-00-00_pm.zipCheck the Main Server and Analytics Server running status –stop them if already running using the below commands:
systemctl stop ft-main-server
systemctl stop ft-analytics-serverLogin to the PostgreSQL database console(using root), delete the current database and create a new one. Command:
su postgresCommand:
psqlRun the query to drop the database.
drop database flotoitsmdb;Run the query to create a new database.
create database flotoitsmdb;Once created, verify whether the database is created using the below command:
\lQuit from the database using the below command:
\qRestore the database dump file into the newly created one.
Command:
pg_restore –U postgres –d flotoitsmdb < DB_DATE_BACKUPExample:
pg_restore -U postgres -d flotoitsmdb < DB_10-6-2021_11-00-00_pm