Motadata High Availability Server Setup
What is High Availability Setup?
High availability refers to the systems that are durable and likely to operate continuously without failure for a long time. HA aims to ensure an agreed level of operational performance, usually uptime, for a higher than normal period by ensuring service and data recovery during an unplanned disruption.
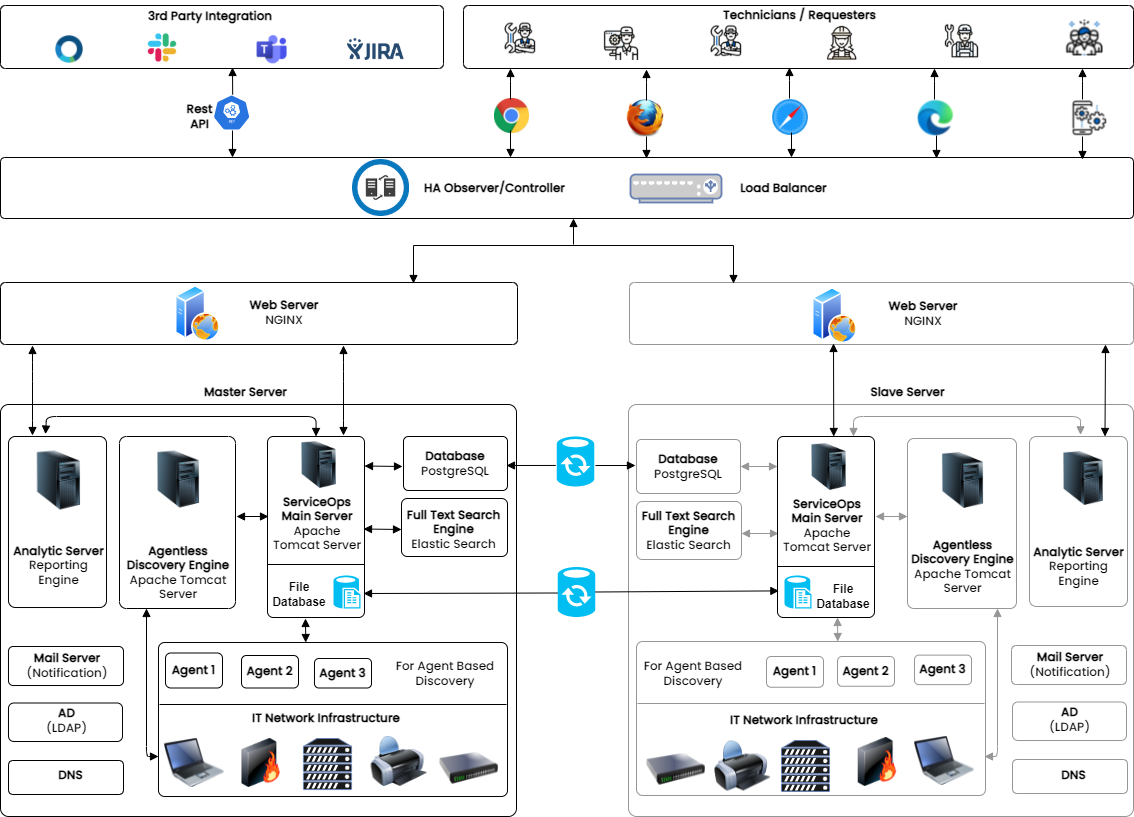
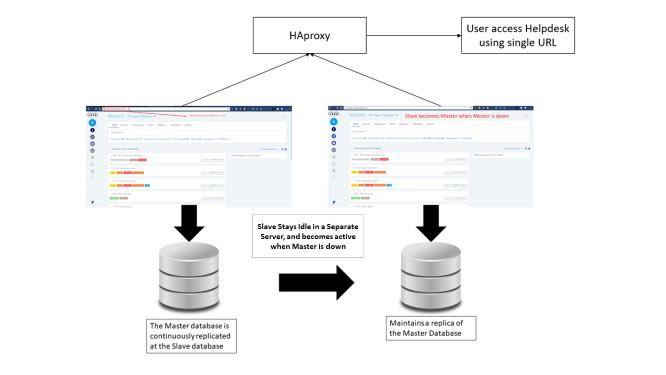
In a High Availability setup, there are mainly 3 servers such as, the main server which is called as ‘Master’, the secondary server which is called as Slave and the other is an HA-proxy Server.
Master is the main (IT Service Desk) server which is accessed by the users, and the Slave remains idle. The data of the Master’s database is continuously replicated in the Slave side’s database. During downtime, Slave becomes the Master with its synced Database same as the Master (Main Server).
Both Master and Slave are connected to the HA-proxy server. The proxy server acts as a load balancer that redirects traffic to the Slave when the Master is down.
For example, An organization maintaining an HA has to have two separate Servers, one for Master and other for Slave, this is to ensure that in an unforeseen event like a fire, natural calamity, etc. when the Master is down, the Slave can be kept alive from the last point of recovery.
- High Availability setup can be used for a planned outage of the Service Desk for the purpose of maintenance.
- High Availability can be used in the event of a disaster recovery of data.
Minimum Hardware Requirements for HA Observer and HA Proxy
You have to install the product build in two separate servers (with different environments), one as the Master and other as the Slave. Both the servers have to have separate IP addresses.
- Minimum 4GB of System RAM
- Minimum Four Core Processor
- Minimum 100 GB of Hard disk space
- Need high speed connectivity between Master, Slave and HA Observer
- Minimum 150 Mbps+ continuous Disk I/O speed is required
Prerequisites
- ServiceOps same version must be installed on Master and Slave machine
- Allow ICMP protocol between Master, Slave, and Observer server
- Allow SSH (22) port access from Observer to Master, Slave server
- Allow Postgress database (5432) port access between master-slave server
- Use same username and password for SSH with home directory and have sudo permission on Master, Slave and HA Observer servers.
Download of Base OS:
You need Ubuntu-18.04 Server OS for this setup. Follow the link to download the OS: Download Link
Installation of Master and Slave
- For Hardware Requirements please refer Hardware Requirements
Copy release build installer (service_desk_master_CI) to target machine.
Open terminal and navigate to the directory where the build is.
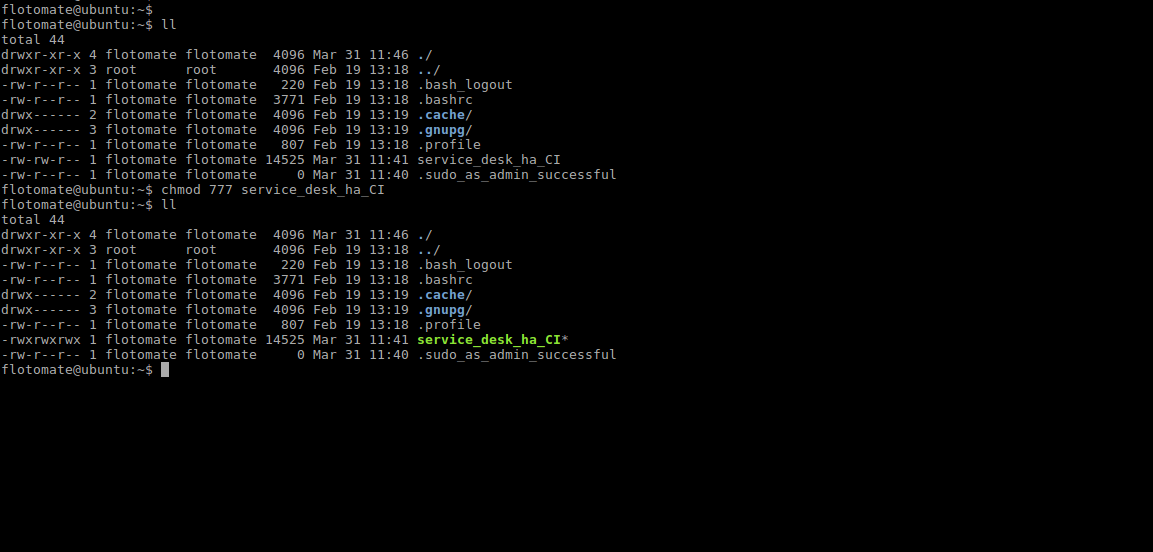
Make Sure you have the permission to execute the file. If there’s no permission then you can change it using the following command:
sudo chmod 777 service_desk_master_CIRun Installer by using the following command:
sudo ./service_desk_master_CIEnter the password when prompted. The password will be the same as the system admin password.
Enter the file where the key needs to be saved. Here, just press enter and it will auto-add the key path.
After adding the ssh key, it will prompt to enter the username for the server ssh
Setting up HA Observer Server
- PLEASE DO NOT USE “sudo” TO INSTALL ‘INSTALLER PACKAGE’
- PLEASE INSTALL ONLY AFTER TWO I.E MASTER AND SLAVE MACHINES ARE READY
- PLEASE USE SAME USERNAME ON SSH MASTER AND SLAVE MACHINE
- PLEASE USE COMMON PASSWORD ON SSH MASTER AND SLAVE MACHINE
Step 1: Download HA Observer build on HA machine.
Step 2: Assign Execute permission using below command:
chmod 777 service_desk_ha_CI
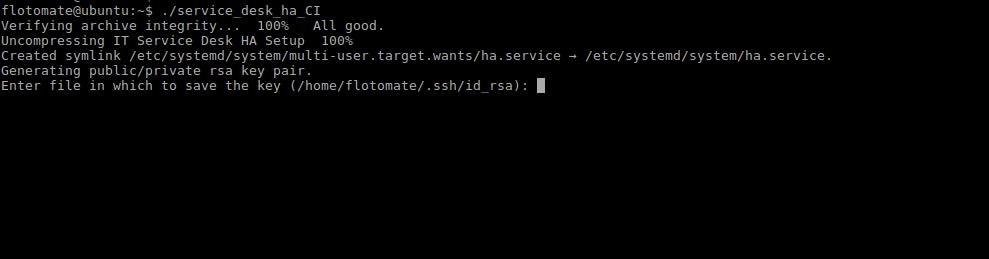
Step 3: Run HA observer build ./service_desk_ha_CI
Step 4: It will prompt for generation of the public key. Press Enter for generating the Key.
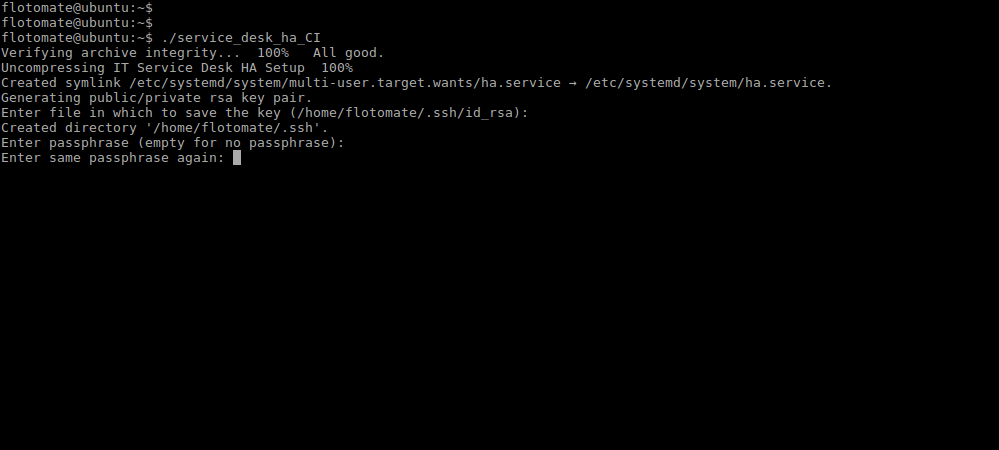
Step 5: After generating public key, it will prompt to enter the Passphrase twice. Press Enter for both the prompts.
Step 6: It will prompt to “Enter username for server ssh”. This Username will be Common for both the machines i.e Master and Slave.
Here flotomate is entered just for example. User needs to enter the respective Machine's Username.
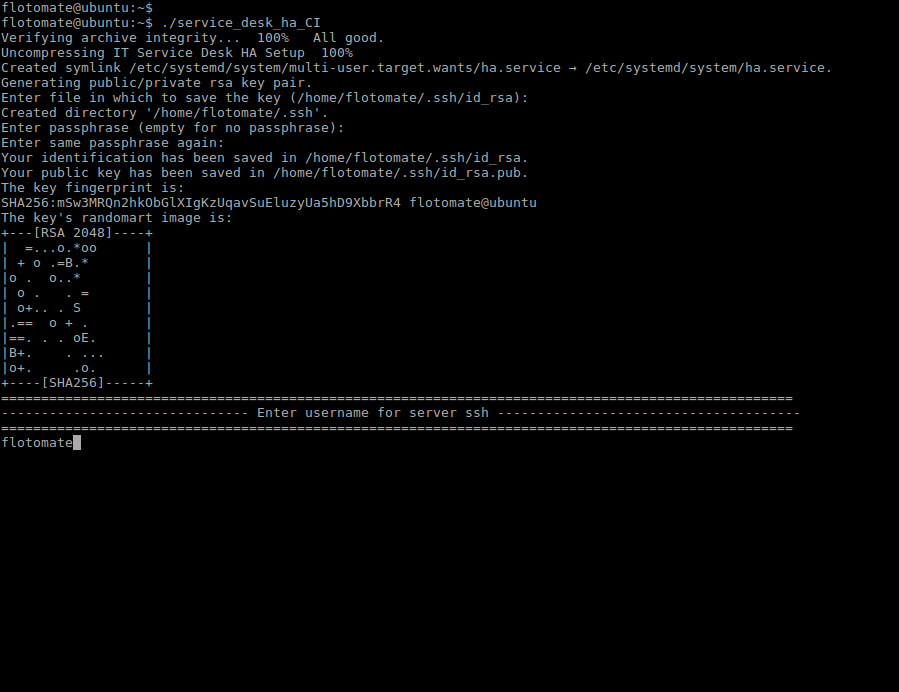
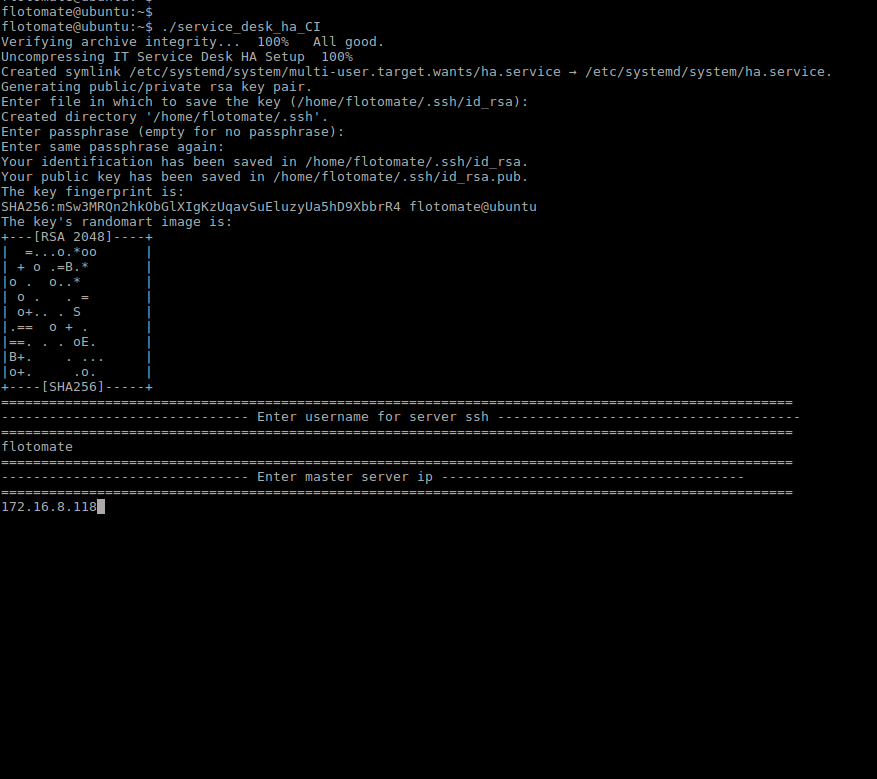
Step 7: Enter the “Master server IP Address”.
Here entered IP is just for example. User needs to enter respective Master’s IP.
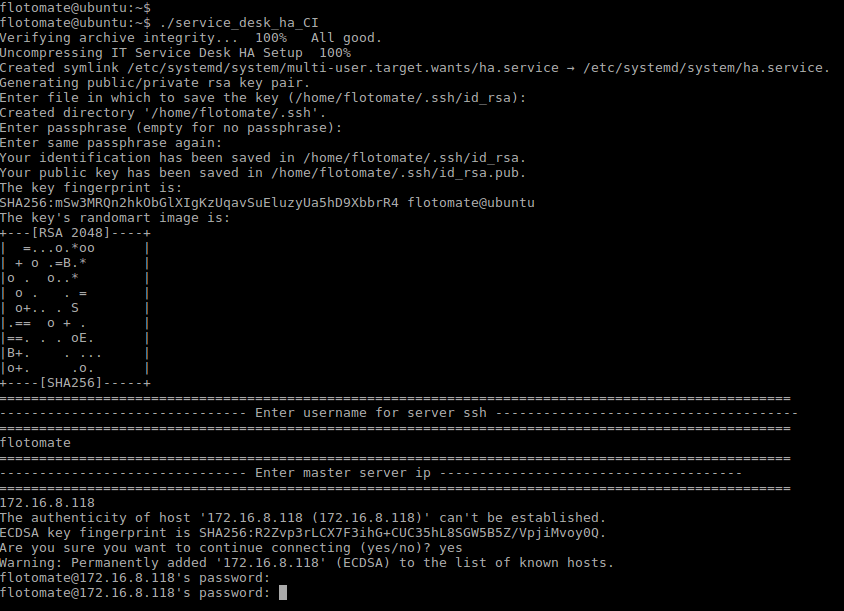
Step 8: After entering the IP Address, it will prompt for Password twice. Here, the password will be respective machines password.
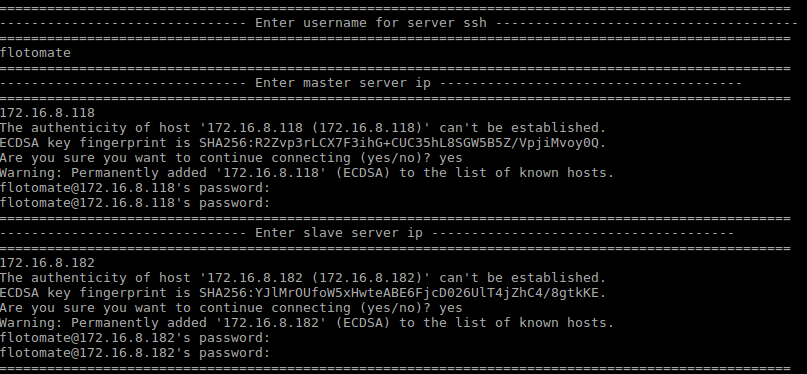
Step 9: It will then prompt to Enter Slave’s Server IP and password.
Step 10: It will then prompt to “Enter sudo password”. This password will be the same as the common password entered in Step 8.
Because this will be Root i.e. Sudo Login, the password will be visible.
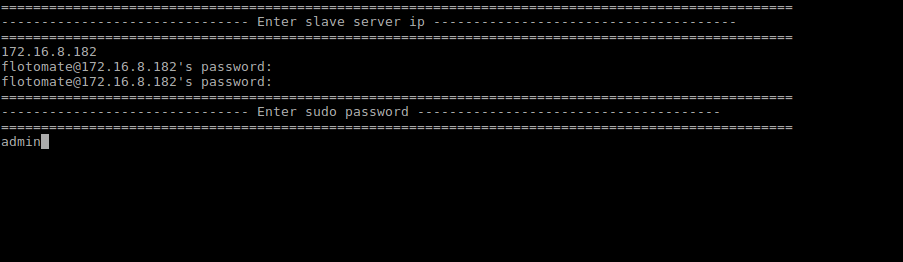
Step 11: After entering the sudo password, it will automatically start configuration of Slave and will show message as “Enter slave config started”.
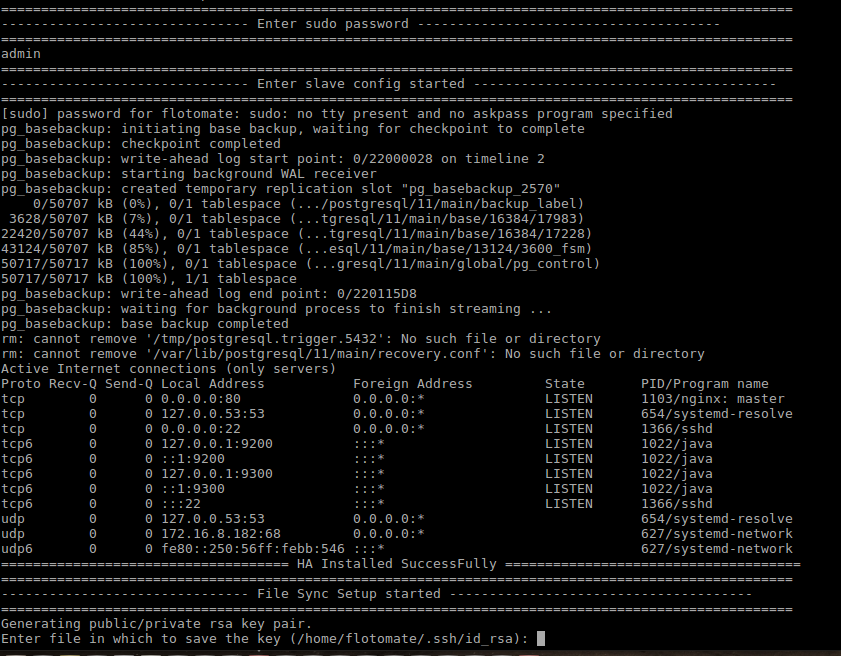
Step 12: After finishing the above step it will show message “HA Installed SuccessFully”. It will then automatically start the mechanism of file sync showing the message “File Sync Setup Started”.
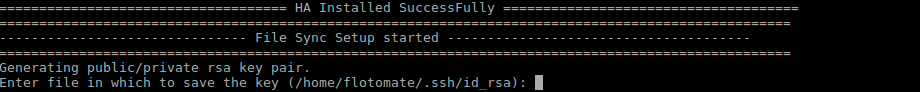
Step 13: After the File Sync Setup started, it will prompt for “Entering Key” for generating public/private rsa key pair. Press Enter in response.
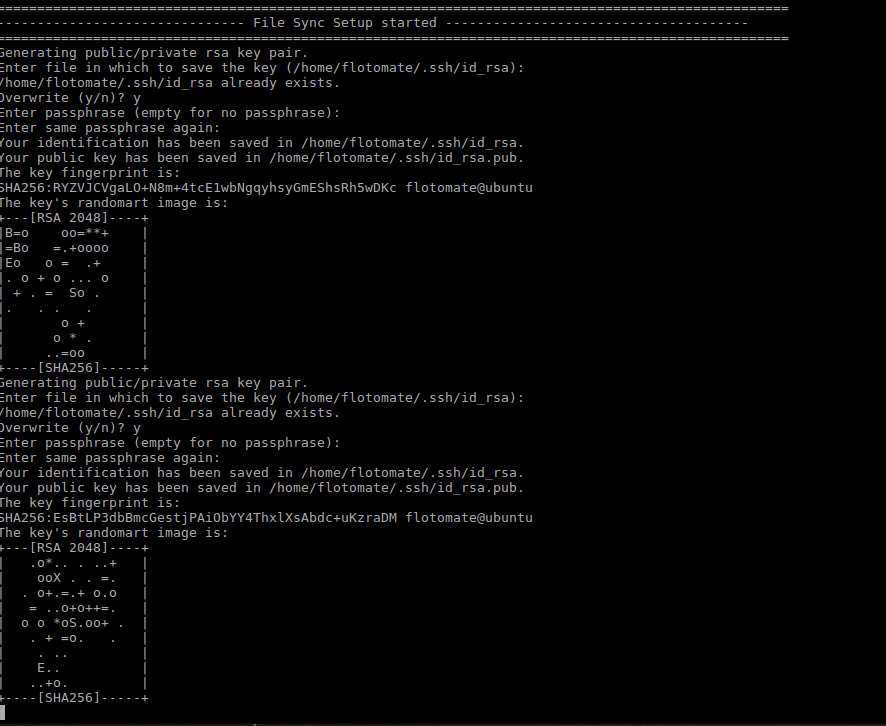
Step 14: After entering the Key, File Sync Installation Setup finishes. With this HA Observer Installation also finishes.
Setting Up HA-Proxy Server
HA-Proxy is a popular open source load balancer. You can use any other load balancer.
The HA-Proxy (also known as a Load Balancer) is a solution to distribute a web application across multiple servers. In the HA setup, a HA-Proxy routes the traffic to the Slave server (after becoming a Master) when the Master is down.
HA-Proxy requires a separate IP. HA-Proxy is a separate server from the Master and Slave.
We will be using HA Proxy stable version for HA setup. Your server needs to have an Internet connection. Run the below commands from the terminal:
apt-get update
apt-get install haproxy
Step-1: Log into the HA proxy server and open a terminal as root.
Step-2: Now you need to configure the Configuration file of HAproxy using the following command.
sudo nano /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
Step-3: Copy paste the following at the end of the file and save it.
defaults
log global
mode tcp
option httplog
option dontlognull
timeout connect 5000
timeout client 50000
timeout server 50000
errorfile 400 /etc/haproxy/errors/400.http
errorfile 403 /etc/haproxy/errors/403.http
errorfile 408 /etc/haproxy/errors/408.http
errorfile 500 /etc/haproxy/errors/500.http
errorfile 502 /etc/haproxy/errors/502.http
errorfile 503 /etc/haproxy/errors/503.http
errorfile 504 /etc/haproxy/errors/504.http
frontend http_front
bind 172.16.8.100:80
stats uri /haproxy?stats
default_backend http_back
backend http_back
balance roundrobin
mode tcp
option tcp-check
server ubuntu 172.16.8.241:80 check port 80
server ubuntu 172.16.8.240:80 check port 80
Step-4: Now you need to restart the HA proxy using the below command:
sudo systemctl restart haproxy
The passive server takes approximately 5-8 minutes to come up when the active server goes down.