1.2.10. Merge Requests¶
Sometimes two or more Requests are similar, or they are duplicates The Merge function in Motadata helps in dealing with duplicates and similar Requests.
In the Merge process, one is the Primary Request, and all others are Secondary. The outcome of a merge is always the Secondary Requests linked to the Primary Request. If the Merge process happens between Requests created by the same Requestor, then all the Secondary Requests are closed, but they stay linked with the Primary Request.
1.2.10.1. Doing a Merge:¶
Log in to the Technician Portal.
Go to Request >> Request List View.
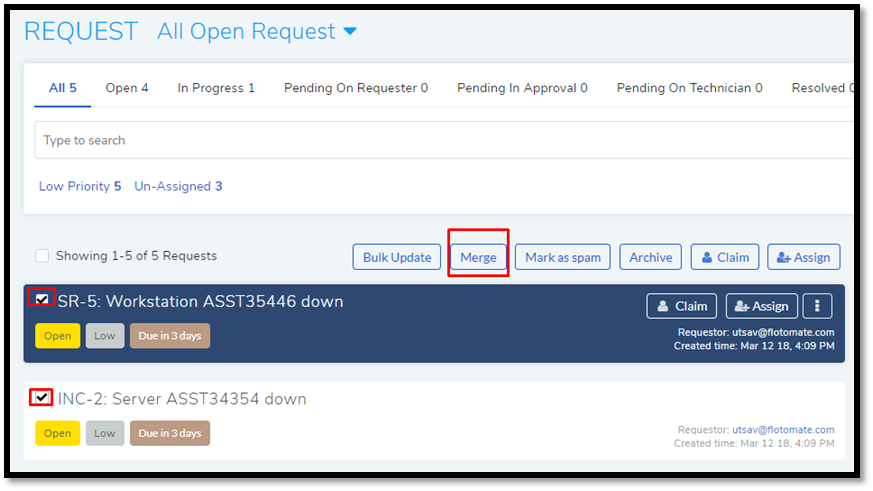
Select two or more Requests, and the Merge option appears over the list area.
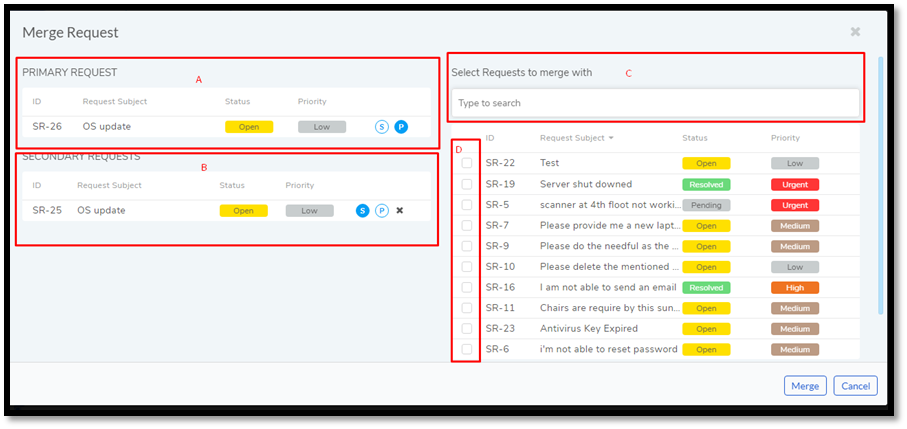
Clicking on Merge takes you to a new dialog box. Here you can choose which one to keep as Primary and which one, Secondary. Referring to
rmf-70, section-A shows the Primary Request (which can only be one) and section-B lists the Secondary. Clicking on the symbol adjacent to a Request (S & P) changes a Request from Primary to Secondary and vice-versa.Section-C is the search area. You can use the search area to find specific Requests by using custom keywords and predefined search options. The Search Box works similarly to the Search Box in List View.
Below the Search Box is a list of other Requests. If no search filter is applied, then the list contains all the other Requests not selected for merge. Section-D allows you to select multiple Requests. The total number of selected Requests appears on top of the Search Box along with the symbol S. Click on the S symbol to add them to the Secondary Request area.
Click Merge once you are done with the setup. The Merge process closes all those Secondary Requests with the same Requestor email, treating them as duplicate, as in the Primary Request.
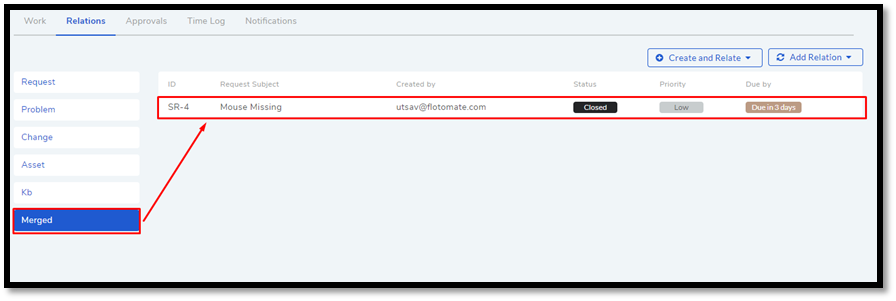
1.2.10.2. Viewing the Relation of a Primary Request:¶
You can see the effect of merge under Relations tab in the Primary Request’s Details View.